Socket
Socket
一、I/O 模型
一个输入操作通常包括两个阶段:
- 等待数据准备好
- 从内核向进程复制数据
对于一个套接字上的输入操作,第一步通常涉及等待数据从网络中到达。当所等待数据到达时,它被复制到内核中的某个缓冲区。第二步就是把数据从内核缓冲区复制到应用进程缓冲区。
Unix 有五种 I/O 模型:
- 阻塞式 I/O
- 非阻塞式 I/O
- I/O 复用(select 和 poll)
- 信号驱动式 I/O(SIGIO)
- 异步 I/O(AIO)
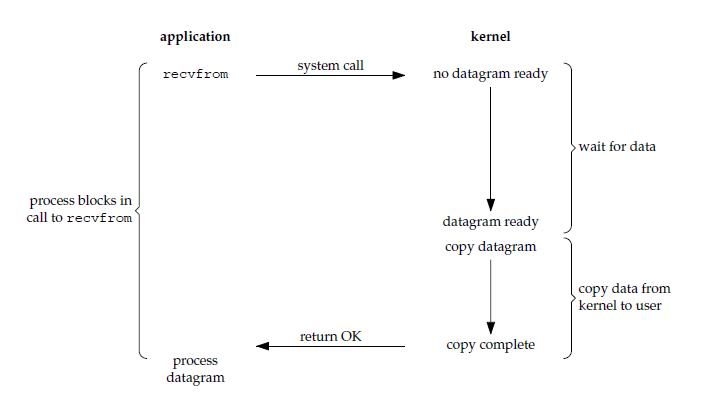
阻塞式 I/O
应用进程被阻塞,直到数据从内核缓冲区复制到应用进程缓冲区中才返回。
应该注意到,在阻塞的过程中,其它应用进程还可以执行,因此阻塞不意味着整个操作系统都被阻塞。因为其它应用进程还可以执行,所以不消耗 CPU 时间,这种模型的 CPU 利用率会比较高。
下图中,recvfrom() 用于接收 Socket 传来的数据,并复制到应用进程的缓冲区 buf 中。这里把 recvfrom() 当成系统调用。
ssize_t recvfrom(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len, int flags, struct sockaddr *src_addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
非阻塞式 I/O
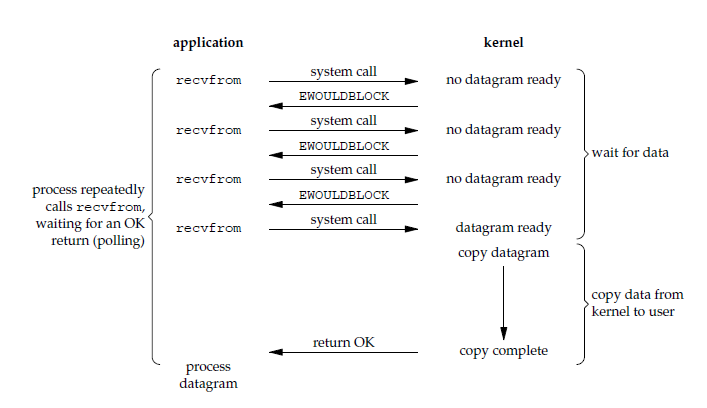
应用进程执行系统调用之后,内核返回一个错误码。应用进程可以继续执行,但是需要不断的执行系统调用来获知 I/O 是否完成,这种方式称为轮询(polling)。
由于 CPU 要处理更多的系统调用,因此这种模型的 CPU 利用率比较低。
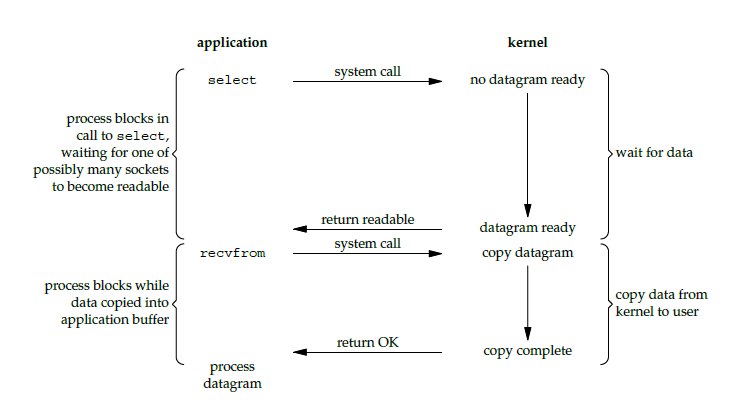
I/O 复用
使用 select 或者 poll 等待数据,并且可以等待多个套接字中的任何一个变为可读。这一过程会被阻塞,当某一个套接字可读时返回,之后再使用 recvfrom 把数据从内核复制到进程中。
它可以让单个进程具有处理多个 I/O 事件的能力。又被称为 Event Driven I/O,即事件驱动 I/O。
如果一个 Web 服务器没有 I/O 复用,那么每一个 Socket 连接都需要创建一个线程去处理。如果同时有几万个连接,那么就需要创建相同数量的线程。相比于多进程和多线程技术,I/O 复用不需要进程线程创建和切换的开销,系统开销更小。
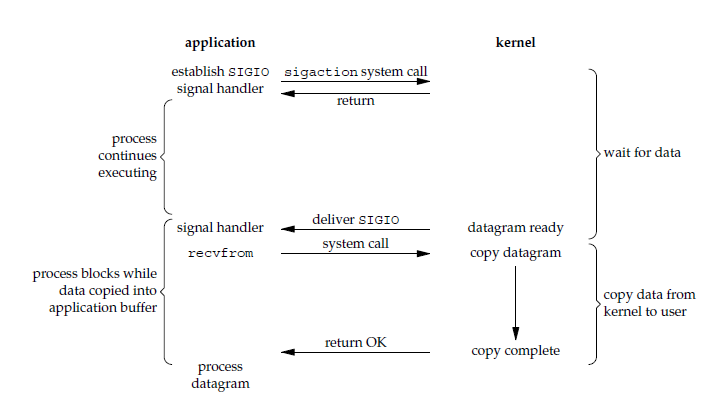
信号驱动 I/O
应用进程使用 sigaction 系统调用,内核立即返回,应用进程可以继续执行,也就是说等待数据阶段应用进程是非阻塞的。内核在数据到达时向应用进程发送 SIGIO 信号,应用进程收到之后在信号处理程序中调用 recvfrom 将数据从内核复制到应用进程中。
相比于非阻塞式 I/O 的轮询方式,信号驱动 I/O 的 CPU 利用率更高。
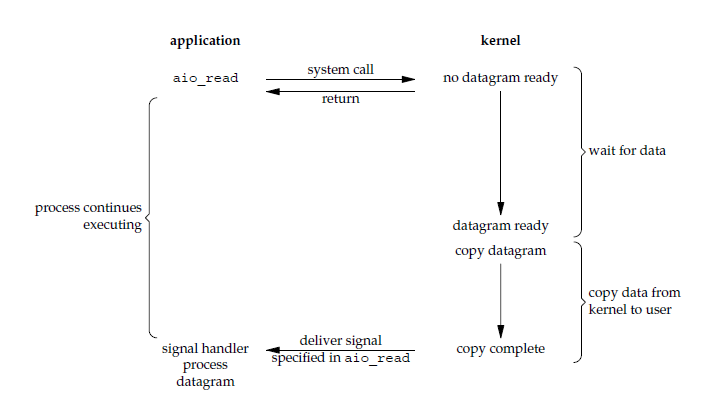
异步 I/O
应用进程执行 aio_read 系统调用会立即返回,应用进程可以继续执行,不会被阻塞,内核会在所有操作完成之后向应用进程发送信号。
异步 I/O 与信号驱动 I/O 的区别在于,异步 I/O 的信号是通知应用进程 I/O 完成,而信号驱动 I/O 的信号是通知应用进程可以开始 I/O。
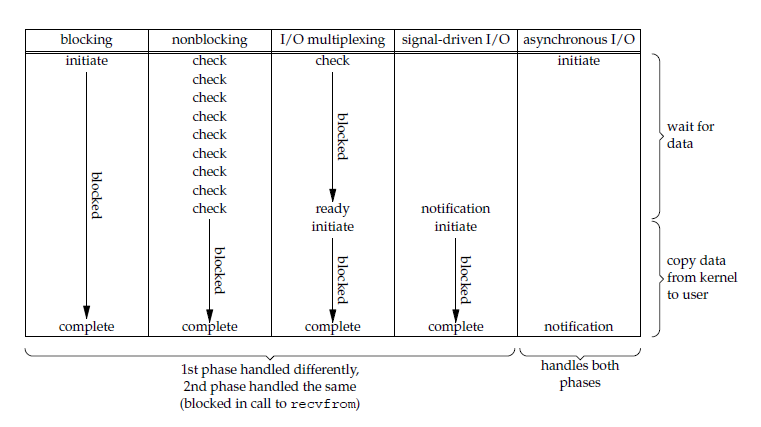
五大 I/O 模型比较
- 同步 I/O:将数据从内核缓冲区复制到应用进程缓冲区的阶段(第二阶段),应用进程会阻塞。
- 异步 I/O:第二阶段应用进程不会阻塞。
同步 I/O 包括阻塞式 I/O、非阻塞式 I/O、I/O 复用和信号驱动 I/O ,它们的主要区别在第一个阶段。
非阻塞式 I/O 、信号驱动 I/O 和异步 I/O 在第一阶段不会阻塞。
二、I/O 复用
select/poll/epoll 都是 I/O 多路复用的具体实现,select 出现的最早,之后是 poll,再是 epoll。
select
int select(int n, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
select 允许应用程序监视一组文件描述符,等待一个或者多个描述符成为就绪状态,从而完成 I/O 操作。
fd_set 使用数组实现,数组大小使用 FD_SETSIZE 定义,所以只能监听少于 FD_SETSIZE 数量的描述符。有三种类型的描述符类型:readset、writeset、exceptset,分别对应读、写、异常条件的描述符集合。
timeout 为超时参数,调用 select 会一直阻塞直到有描述符的事件到达或者等待的时间超过 timeout。
成功调用返回结果大于 0,出错返回结果为 -1,超时返回结果为 0。
fd_set fd_in, fd_out;
struct timeval tv;
// Reset the sets
FD_ZERO( &fd_in );
FD_ZERO( &fd_out );
// Monitor sock1 for input events
FD_SET( sock1, &fd_in );
// Monitor sock2 for output events
FD_SET( sock2, &fd_out );
// Find out which socket has the largest numeric value as select requires it
int largest_sock = sock1 > sock2 ? sock1 : sock2;
// Wait up to 10 seconds
tv.tv_sec = 10;
tv.tv_usec = 0;
// Call the select
int ret = select( largest_sock + 1, &fd_in, &fd_out, NULL, &tv );
// Check if select actually succeed
if ( ret == -1 )
// report error and abort
else if ( ret == 0 )
// timeout; no event detected
else
{
if ( FD_ISSET( sock1, &fd_in ) )
// input event on sock1
if ( FD_ISSET( sock2, &fd_out ) )
// output event on sock2
}
poll
int poll(struct pollfd *fds, unsigned int nfds, int timeout);
poll 的功能与 select 类似,也是等待一组描述符中的一个成为就绪状态。
poll 中的描述符是 pollfd 类型的数组,pollfd 的定义如下:
struct pollfd {
int fd; /* file descriptor */
short events; /* requested events */
short revents; /* returned events */
};
// The structure for two events
struct pollfd fds[2];
// Monitor sock1 for input
fds[0].fd = sock1;
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
// Monitor sock2 for output
fds[1].fd = sock2;
fds[1].events = POLLOUT;
// Wait 10 seconds
int ret = poll( &fds, 2, 10000 );
// Check if poll actually succeed
if ( ret == -1 )
// report error and abort
else if ( ret == 0 )
// timeout; no event detected
else
{
// If we detect the event, zero it out so we can reuse the structure
if ( fds[0].revents & POLLIN )
fds[0].revents = 0;
// input event on sock1
if ( fds[1].revents & POLLOUT )
fds[1].revents = 0;
// output event on sock2
}
比较
1. 功能
select 和 poll 的功能基本相同,不过在一些实现细节上有所不同。
- select 会修改描述符,而 poll 不会;
- select 的描述符类型使用数组实现,FD_SETSIZE 大小默认为 1024,因此默认只能监听少于 1024 个描述符。如果要监听更多描述符的话,需要修改 FD_SETSIZE 之后重新编译;而 poll 没有描述符数量的限制;
- poll 提供了更多的事件类型,并且对描述符的重复利用上比 select 高。
- 如果一个线程对某个描述符调用了 select 或者 poll,另一个线程关闭了该描述符,会导致调用结果不确定。
2. 速度
select 和 poll 速度都比较慢,每次调用都需要将全部描述符从应用进程缓冲区复制到内核缓冲区。
3. 可移植性
几乎所有的系统都支持 select,但是只有比较新的系统支持 poll。
epoll
int epoll_create(int size);
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event * events, int maxevents, int timeout);
epoll_ctl() 用于向内核注册新的描述符或者是改变某个文件描述符的状态。已注册的描述符在内核中会被维护在一棵红黑树上,通过回调函数内核会将 I/O 准备好的描述符加入到一个链表中管理,进程调用 epoll_wait() 便可以得到事件完成的描述符。
从上面的描述可以看出,epoll 只需要将描述符从进程缓冲区向内核缓冲区拷贝一次,并且进程不需要通过轮询来获得事件完成的描述符。
epoll 仅适用于 Linux OS。
epoll 比 select 和 poll 更加灵活而且没有描述符数量限制。
epoll 对多线程编程更有友好,一个线程调用了 epoll_wait() 另一个线程关闭了同一个描述符也不会产生像 select 和 poll 的不确定情况。
// Create the epoll descriptor. Only one is needed per app, and is used to monitor all sockets.
// The function argument is ignored (it was not before, but now it is), so put your favorite number here
int pollingfd = epoll_create( 0xCAFE );
if ( pollingfd < 0 )
// report error
// Initialize the epoll structure in case more members are added in future
struct epoll_event ev = { 0 };
// Associate the connection class instance with the event. You can associate anything
// you want, epoll does not use this information. We store a connection class pointer, pConnection1
ev.data.ptr = pConnection1;
// Monitor for input, and do not automatically rearm the descriptor after the event
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLONESHOT;
// Add the descriptor into the monitoring list. We can do it even if another thread is
// waiting in epoll_wait - the descriptor will be properly added
if ( epoll_ctl( epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, pConnection1->getSocket(), &ev ) != 0 )
// report error
// Wait for up to 20 events (assuming we have added maybe 200 sockets before that it may happen)
struct epoll_event pevents[ 20 ];
// Wait for 10 seconds, and retrieve less than 20 epoll_event and store them into epoll_event array
int ready = epoll_wait( pollingfd, pevents, 20, 10000 );
// Check if epoll actually succeed
if ( ret == -1 )
// report error and abort
else if ( ret == 0 )
// timeout; no event detected
else
{
// Check if any events detected
for ( int i = 0; i < ready; i++ )
{
if ( pevents[i].events & EPOLLIN )
{
// Get back our connection pointer
Connection * c = (Connection*) pevents[i].data.ptr;
c->handleReadEvent();
}
}
}
工作模式
epoll 的描述符事件有两种触发模式:LT(level trigger)和 ET(edge trigger)。
1. LT 模式
当 epoll_wait() 检测到描述符事件到达时,将此事件通知进程,进程可以不立即处理该事件,下次调用 epoll_wait() 会再次通知进程。是默认的一种模式,并且同时支持 Blocking 和 No-Blocking。
2. ET 模式
和 LT 模式不同的是,通知之后进程必须立即处理事件,下次再调用 epoll_wait() 时不会再得到事件到达的通知。
很大程度上减少了 epoll 事件被重复触发的次数,因此效率要比 LT 模式高。只支持 No-Blocking,以避免由于一个文件句柄的阻塞读/阻塞写操作把处理多个文件描述符的任务饿死。
应用场景
很容易产生一种错觉认为只要用 epoll 就可以了,select 和 poll 都已经过时了,其实它们都有各自的使用场景。
1. select 应用场景
select 的 timeout 参数精度为微秒,而 poll 和 epoll 为毫秒,因此 select 更加适用于实时性要求比较高的场景,比如核反应堆的控制。
select 可移植性更好,几乎被所有主流平台所支持。
2. poll 应用场景
poll 没有最大描述符数量的限制,如果平台支持并且对实时性要求不高,应该使用 poll 而不是 select。
3. epoll 应用场景
只需要运行在 Linux 平台上,有大量的描述符需要同时轮询,并且这些连接最好是长连接。
需要同时监控小于 1000 个描述符,就没有必要使用 epoll,因为这个应用场景下并不能体现 epoll 的优势。
需要监控的描述符状态变化多,而且都是非常短暂的,也没有必要使用 epoll。因为 epoll 中的所有描述符都存储在内核中,造成每次需要对描述符的状态改变都需要通过 epoll_ctl() 进行系统调用,频繁系统调用降低效率。并且 epoll 的描述符存储在内核,不容易调试。
参考资料
- Stevens W R, Fenner B, Rudoff A M. UNIX network programming[M]. Addison-Wesley Professional, 2004.
- http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/select.2.html
- http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/poll.2.html
- Boost application performance using asynchronous I/O
- Synchronous and Asynchronous I/O
- Linux IO 模式及 select、poll、epoll 详解
- poll vs select vs event-based
- select / poll / epoll: practical difference for system architects
- Browse the source code of userspace/glibc/sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/ online
