Java 容器
Java 容器
一、概览
容器主要包括 Collection 和 Map 两种,Collection 存储着对象的集合,而 Map 存储着键值对(两个对象)的映射表。
Collection

1. Set
TreeSet:基于红黑树实现,支持有序性操作,例如根据一个范围查找元素的操作。但是查找效率不如 HashSet,HashSet 查找的时间复杂度为 O(1),TreeSet 则为 O(logN)。
HashSet:基于哈希表实现,支持快速查找,但不支持有序性操作。并且失去了元素的插入顺序信息,也就是说使用 Iterator 遍历 HashSet 得到的结果是不确定的。
LinkedHashSet:具有 HashSet 的查找效率,并且内部使用双向链表维护元素的插入顺序。
2. List
ArrayList:基于动态数组实现,支持随机访问。
Vector:和 ArrayList 类似,但它是线程安全的。
LinkedList:基于双向链表实现,只能顺序访问,但是可以快速地在链表中间插入和删除元素。不仅如此,LinkedList 还可以用作栈、队列和双向队列。
3. Queue
LinkedList:可以用它来实现双向队列。
PriorityQueue:基于堆结构实现,可以用它来实现优先队列。
Map
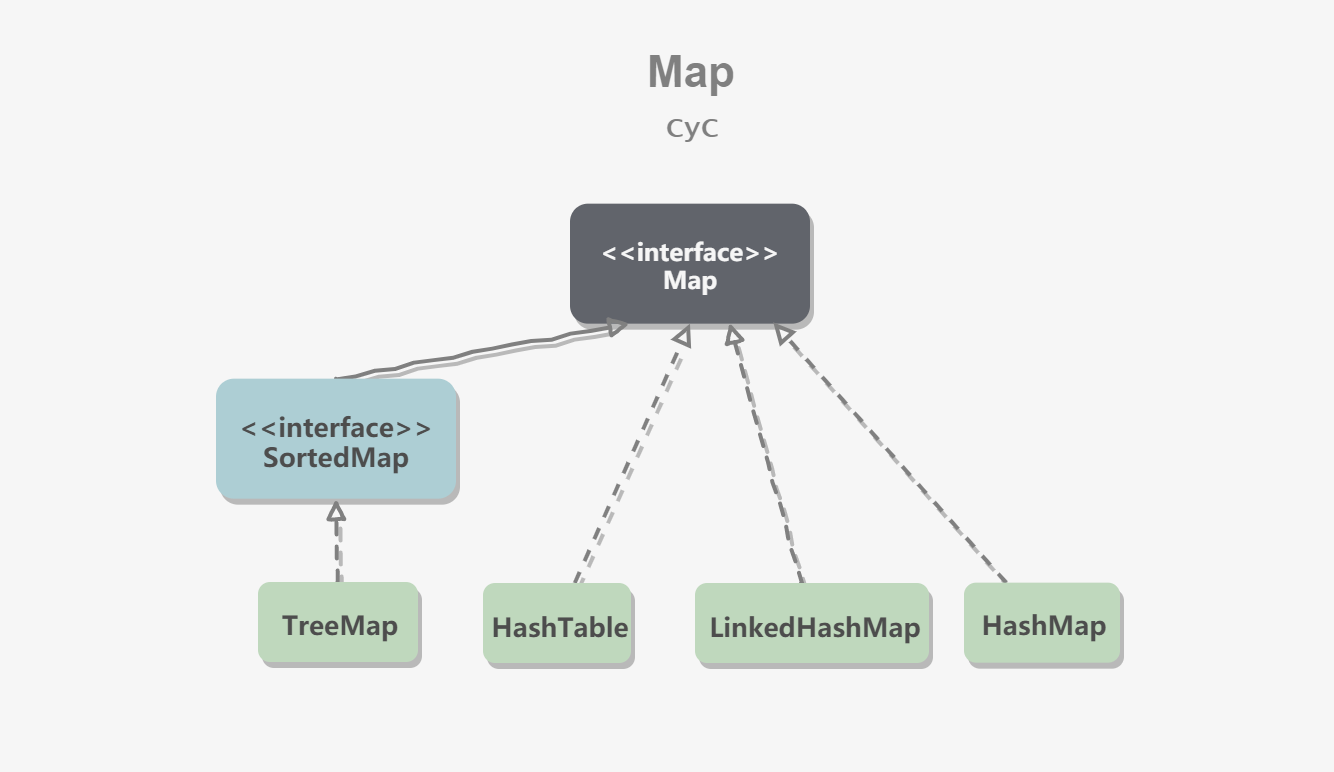
TreeMap:基于红黑树实现。
HashMap:基于哈希表实现。
HashTable:和 HashMap 类似,但它是线程安全的,这意味着同一时刻多个线程同时写入 HashTable 不会导致数据不一致。它是遗留类,不应该去使用它,而是使用 ConcurrentHashMap 来支持线程安全,ConcurrentHashMap 的效率会更高,因为 ConcurrentHashMap 引入了分段锁。
LinkedHashMap:使用双向链表来维护元素的顺序,顺序为插入顺序或者最近最少使用(LRU)顺序。
二、容器中的设计模式
迭代器模式
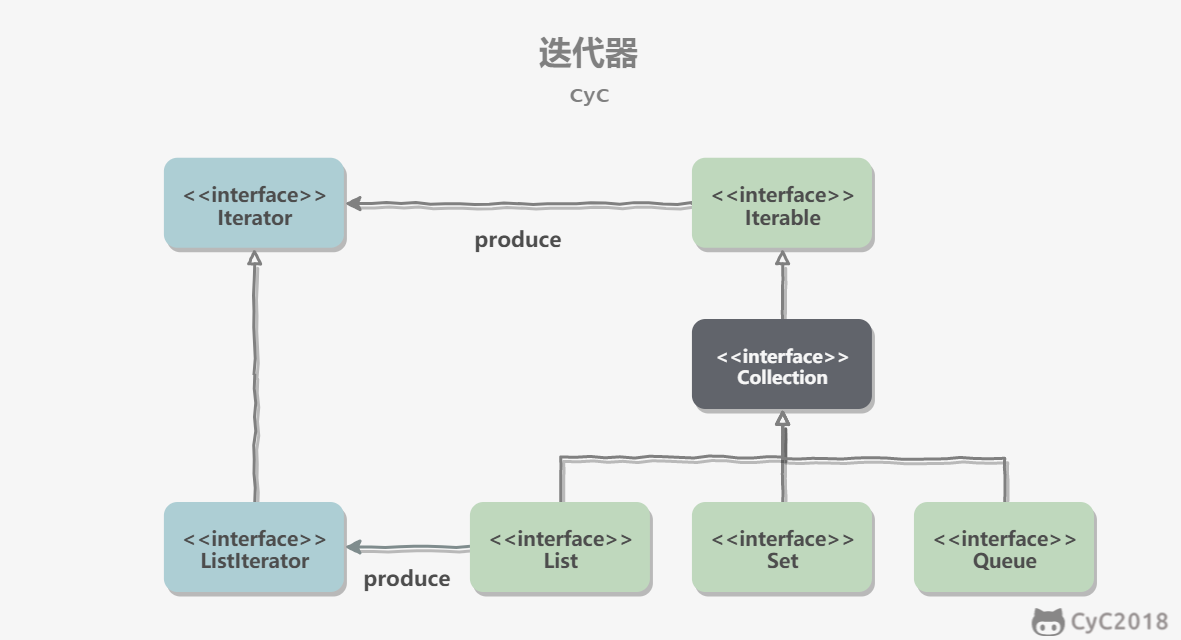
Collection 继承了 Iterable 接口,其中的 iterator() 方法能够产生一个 Iterator 对象,通过这个对象就可以迭代遍历 Collection 中的元素。
从 JDK 1.5 之后可以使用 foreach 方法来遍历实现了 Iterable 接口的聚合对象。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
for (String item : list) {
System.out.println(item);
}
适配器模式
java.util.Arrays#asList() 可以把数组类型转换为 List 类型。
@SafeVarargs
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a)
应该注意的是 asList() 的参数为泛型的变长参数,不能使用基本类型数组作为参数,只能使用相应的包装类型数组。
Integer[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
List list = Arrays.asList(arr);
也可以使用以下方式调用 asList():
List list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);
三、源码分析
如果没有特别说明,以下源码分析基于 JDK 1.8。
在 IDEA 中 double shift 调出 Search EveryWhere,查找源码文件,找到之后就可以阅读源码。
ArrayList
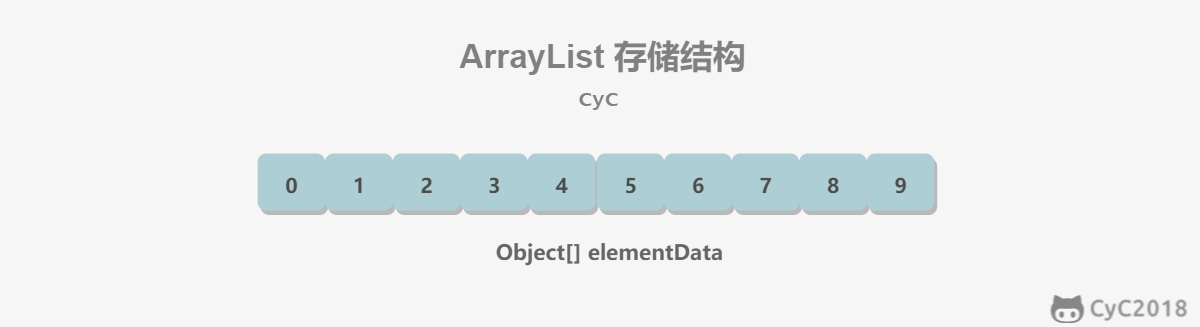
1. 概览
因为 ArrayList 是基于数组实现的,所以支持快速随机访问。RandomAccess 接口标识着该类支持快速随机访问。
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
数组的默认大小为 10。
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
2. 扩容
添加元素时使用 ensureCapacityInternal() 方法来保证容量足够,如果不够时,需要使用 grow() 方法进行扩容,新容量的大小为 oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1),即 oldCapacity+oldCapacity/2。其中 oldCapacity >> 1 需要取整,所以新容量大约是旧容量的 1.5 倍左右。(oldCapacity 为偶数就是 1.5 倍,为奇数就是 1.5 倍-0.5)
扩容操作需要调用 Arrays.copyOf() 把原数组整个复制到新数组中,这个操作代价很高,因此最好在创建 ArrayList 对象时就指定大概的容量大小,减少扩容操作的次数。
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
3. 删除元素
需要调用 System.arraycopy() 将 index+1 后面的元素都复制到 index 位置上,该操作的时间复杂度为 O(N),可以看到 ArrayList 删除元素的代价是非常高的。
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
4. 序列化
ArrayList 基于数组实现,并且具有动态扩容特性,因此保存元素的数组不一定都会被使用,那么就没必要全部进行序列化。
保存元素的数组 elementData 使用 transient 修饰,该关键字声明数组默认不会被序列化。
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
ArrayList 实现了 writeObject() 和 readObject() 来控制只序列化数组中有元素填充那部分内容。
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in capacity
s.readInt(); // ignored
if (size > 0) {
// be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity
ensureCapacityInternal(size);
Object[] a = elementData;
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
a[i] = s.readObject();
}
}
}
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException{
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone()
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
s.writeObject(elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
序列化时需要使用 ObjectOutputStream 的 writeObject() 将对象转换为字节流并输出。而 writeObject() 方法在传入的对象存在 writeObject() 的时候会去反射调用该对象的 writeObject() 来实现序列化。反序列化使用的是 ObjectInputStream 的 readObject() 方法,原理类似。
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
oos.writeObject(list);
5. Fail-Fast
modCount 用来记录 ArrayList 结构发生变化的次数。结构发生变化是指添加或者删除至少一个元素的所有操作,或者是调整内部数组的大小,仅仅只是设置元素的值不算结构发生变化。
在进行序列化或者迭代等操作时,需要比较操作前后 modCount 是否改变,如果改变了需要抛出 ConcurrentModificationException。代码参考上节序列化中的 writeObject() 方法。
Vector
1. 同步
它的实现与 ArrayList 类似,但是使用了 synchronized 进行同步。
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return elementData(index);
}
2. 扩容
Vector 的构造函数可以传入 capacityIncrement 参数,它的作用是在扩容时使容量 capacity 增长 capacityIncrement。如果这个参数的值小于等于 0,扩容时每次都令 capacity 为原来的两倍。
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
调用没有 capacityIncrement 的构造函数时,capacityIncrement 值被设置为 0,也就是说默认情况下 Vector 每次扩容时容量都会翻倍。
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
3. 与 ArrayList 的比较
- Vector 是同步的,因此开销就比 ArrayList 要大,访问速度更慢。最好使用 ArrayList 而不是 Vector,因为同步操作完全可以由程序员自己来控制;
- Vector 每次扩容请求其大小的 2 倍(也可以通过构造函数设置增长的容量),而 ArrayList 是 1.5 倍。
4. 替代方案
可以使用 Collections.synchronizedList(); 得到一个线程安全的 ArrayList。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> synList = Collections.synchronizedList(list);
也可以使用 concurrent 并发包下的 CopyOnWriteArrayList 类。
List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
CopyOnWriteArrayList
1. 读写分离
写操作在一个复制的数组上进行,读操作还是在原始数组中进行,读写分离,互不影响。
写操作需要加锁,防止并发写入时导致写入数据丢失。
写操作结束之后需要把原始数组指向新的复制数组。
public boolean add(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
int len = elements.length;
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);
newElements[len] = e;
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
final void setArray(Object[] a) {
array = a;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private E get(Object[] a, int index) {
return (E) a[index];
}
2. 适用场景
CopyOnWriteArrayList 在写操作的同时允许读操作,大大提高了读操作的性能,因此很适合读多写少的应用场景。
但是 CopyOnWriteArrayList 有其缺陷:
- 内存占用:在写操作时需要复制一个新的数组,使得内存占用为原来的两倍左右;
- 数据不一致:读操作不能读取实时性的数据,因为部分写操作的数据还未同步到读数组中。
所以 CopyOnWriteArrayList 不适合内存敏感以及对实时性要求很高的场景。
LinkedList
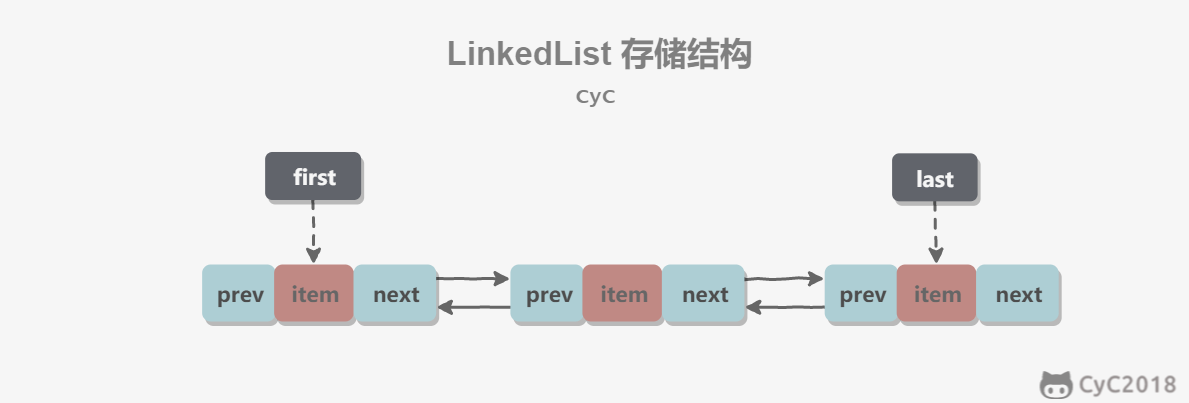
1. 概览
基于双向链表实现,使用 Node 存储链表节点信息。
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
}
每个链表存储了 first 和 last 指针:
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
2. 与 ArrayList 的比较
ArrayList 基于动态数组实现,LinkedList 基于双向链表实现。ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的区别可以归结为数组和链表的区别:
- 数组支持随机访问,但插入删除的代价很高,需要移动大量元素;
- 链表不支持随机访问,但插入删除只需要改变指针。
HashMap
为了便于理解,以下源码分析以 JDK 1.7 为主。
1. 存储结构
内部包含了一个 Entry 类型的数组 table。Entry 存储着键值对。它包含了四个字段,从 next 字段我们可以看出 Entry 是一个链表。即数组中的每个位置被当成一个桶,一个桶存放一个链表。HashMap 使用拉链法来解决冲突,同一个链表中存放哈希值和散列桶取模运算结果相同的 Entry。
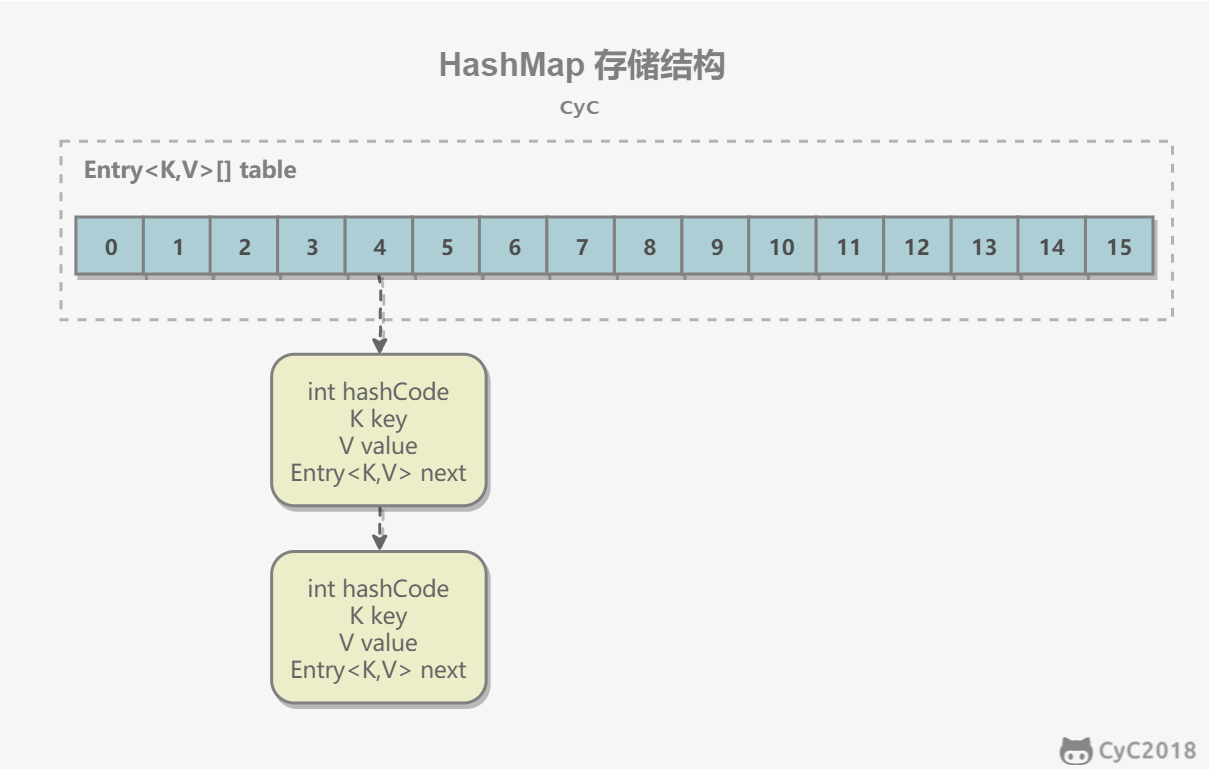
transient Entry[] table;
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(getKey()) ^ Objects.hashCode(getValue());
}
public final String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
}
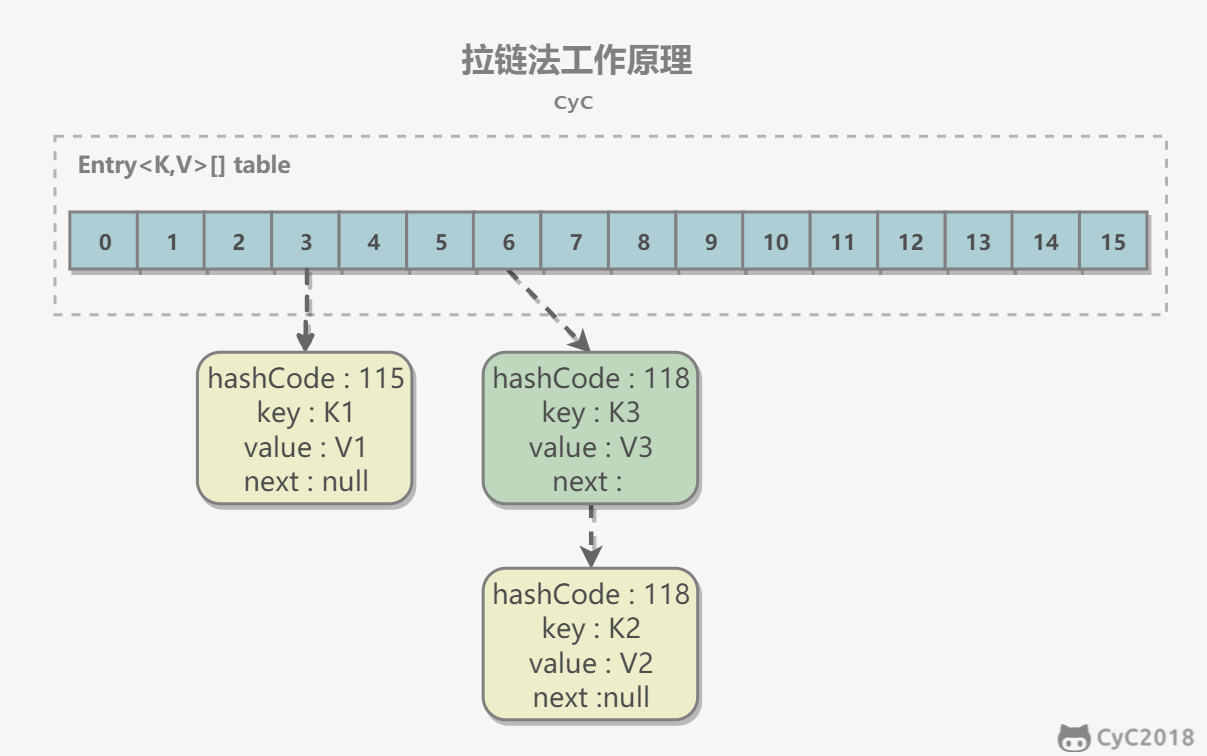
2. 拉链法的工作原理
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("K1", "V1");
map.put("K2", "V2");
map.put("K3", "V3");
- 新建一个 HashMap,默认大小为 16;
- 插入 <K1,V1> 键值对,先计算 K1 的 hashCode 为 115,使用除留余数法得到所在的桶下标 115%16=3。
- 插入 <K2,V2> 键值对,先计算 K2 的 hashCode 为 118,使用除留余数法得到所在的桶下标 118%16=6。
- 插入 <K3,V3> 键值对,先计算 K3 的 hashCode 为 118,使用除留余数法得到所在的桶下标 118%16=6,插在 <K2,V2> 前面。
应该注意到链表的插入是以头插法方式进行的,例如上面的 <K3,V3> 不是插在 <K2,V2> 后面,而是插入在链表头部。
查找需要分成两步进行:
- 计算键值对所在的桶;
- 在链表上顺序查找,时间复杂度显然和链表的长度成正比。
3. put 操作
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
// 键为 null 单独处理
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
// 确定桶下标
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 先找出是否已经存在键为 key 的键值对,如果存在的话就更新这个键值对的值为 value
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
// 插入新键值对
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
HashMap 允许插入键为 null 的键值对。但是因为无法调用 null 的 hashCode() 方法,也就无法确定该键值对的桶下标,只能通过强制指定一个桶下标来存放。HashMap 使用第 0 个桶存放键为 null 的键值对。
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
使用链表的头插法,也就是新的键值对插在链表的头部,而不是链表的尾部。
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
// 头插法,链表头部指向新的键值对
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
4. 确定桶下标
很多操作都需要先确定一个键值对所在的桶下标。
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
4.1 计算 hash 值
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
4.2 取模
令 x = 1<<4,即 x 为 2 的 4 次方,它具有以下性质:
x : 00010000
x-1 : 00001111
令一个数 y 与 x-1 做与运算,可以去除 y 位级表示的第 4 位以上数:
y : 10110010
x-1 : 00001111
y&(x-1) : 00000010
这个性质和 y 对 x 取模效果是一样的:
y : 10110010
x : 00010000
y%x : 00000010
我们知道,位运算的代价比求模运算小的多,因此在进行这种计算时用位运算的话能带来更高的性能。
确定桶下标的最后一步是将 key 的 hash 值对桶个数取模:hash%capacity,如果能保证 capacity 为 2 的 n 次方,那么就可以将这个操作转换为位运算。
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
5. 扩容-基本原理
设 HashMap 的 table 长度为 M,需要存储的键值对数量为 N,如果哈希函数满足均匀性的要求,那么每条链表的长度大约为 N/M,因此查找的复杂度为 O(N/M)。
为了让查找的成本降低,应该使 N/M 尽可能小,因此需要保证 M 尽可能大,也就是说 table 要尽可能大。HashMap 采用动态扩容来根据当前的 N 值来调整 M 值,使得空间效率和时间效率都能得到保证。
和扩容相关的参数主要有:capacity、size、threshold 和 load_factor。
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| capacity | table 的容量大小,默认为 16。需要注意的是 capacity 必须保证为 2 的 n 次方。 |
| size | 键值对数量。 |
| threshold | size 的临界值,当 size 大于等于 threshold 就必须进行扩容操作。 |
| loadFactor | 装载因子,table 能够使用的比例,threshold = (int)(capacity* loadFactor)。 |
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
transient Entry[] table;
transient int size;
int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
transient int modCount;
从下面的添加元素代码中可以看出,当需要扩容时,令 capacity 为原来的两倍。
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
扩容使用 resize() 实现,需要注意的是,扩容操作同样需要把 oldTable 的所有键值对重新插入 newTable 中,因此这一步是很费时的。
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
}
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table;
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;
do {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
6. 扩容-重新计算桶下标
在进行扩容时,需要把键值对重新计算桶下标,从而放到对应的桶上。在前面提到,HashMap 使用 hash%capacity 来确定桶下标。HashMap capacity 为 2 的 n 次方这一特点能够极大降低重新计算桶下标操作的复杂度。
假设原数组长度 capacity 为 16,扩容之后 new capacity 为 32:
capacity : 00010000
new capacity : 00100000
对于一个 Key,它的哈希值 hash 在第 5 位:
- 为 0,那么 hash%00010000 = hash%00100000,桶位置和原来一致;
- 为 1,hash%00010000 = hash%00100000 + 16,桶位置是原位置 + 16。
7. 计算数组容量
HashMap 构造函数允许用户传入的容量不是 2 的 n 次方,因为它可以自动地将传入的容量转换为 2 的 n 次方。
先考虑如何求一个数的掩码,对于 10010000,它的掩码为 11111111,可以使用以下方法得到:
mask |= mask >> 1 11011000
mask |= mask >> 2 11111110
mask |= mask >> 4 11111111
mask+1 是大于原始数字的最小的 2 的 n 次方。
num 10010000
mask+1 100000000
以下是 HashMap 中计算数组容量的代码:
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
8. 链表转红黑树
从 JDK 1.8 开始,一个桶存储的链表长度大于等于 8 时会将链表转换为红黑树。
9. 与 Hashtable 的比较
- Hashtable 使用 synchronized 来进行同步。
- HashMap 可以插入键为 null 的 Entry。
- HashMap 的迭代器是 fail-fast 迭代器。
- HashMap 不能保证随着时间的推移 Map 中的元素次序是不变的。
ConcurrentHashMap
1. 存储结构
static final class HashEntry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V value;
volatile HashEntry<K,V> next;
}
ConcurrentHashMap 和 HashMap 实现上类似,最主要的差别是 ConcurrentHashMap 采用了分段锁(Segment),每个分段锁维护着几个桶(HashEntry),多个线程可以同时访问不同分段锁上的桶,从而使其并发度更高(并发度就是 Segment 的个数)。
Segment 继承自 ReentrantLock。
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L;
static final int MAX_SCAN_RETRIES =
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1 ? 64 : 1;
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
transient int count;
transient int modCount;
transient int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
}
final Segment<K,V>[] segments;
默认的并发级别为 16,也就是说默认创建 16 个 Segment。
static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
2. size 操作
每个 Segment 维护了一个 count 变量来统计该 Segment 中的键值对个数。
/**
* The number of elements. Accessed only either within locks
* or among other volatile reads that maintain visibility.
*/
transient int count;
在执行 size 操作时,需要遍历所有 Segment 然后把 count 累计起来。
ConcurrentHashMap 在执行 size 操作时先尝试不加锁,如果连续两次不加锁操作得到的结果一致,那么可以认为这个结果是正确的。
尝试次数使用 RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK 定义,该值为 2,retries 初始值为 -1,因此尝试次数为 3。
如果尝试的次数超过 3 次,就需要对每个 Segment 加锁。
/**
* Number of unsynchronized retries in size and containsValue
* methods before resorting to locking. This is used to avoid
* unbounded retries if tables undergo continuous modification
* which would make it impossible to obtain an accurate result.
*/
static final int RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK = 2;
public int size() {
// Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to
// continuous async changes in table, resort to locking.
final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments;
int size;
boolean overflow; // true if size overflows 32 bits
long sum; // sum of modCounts
long last = 0L; // previous sum
int retries = -1; // first iteration isn't retry
try {
for (;;) {
// 超过尝试次数,则对每个 Segment 加锁
if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)
ensureSegment(j).lock(); // force creation
}
sum = 0L;
size = 0;
overflow = false;
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) {
Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j);
if (seg != null) {
sum += seg.modCount;
int c = seg.count;
if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0)
overflow = true;
}
}
// 连续两次得到的结果一致,则认为这个结果是正确的
if (sum == last)
break;
last = sum;
}
} finally {
if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)
segmentAt(segments, j).unlock();
}
}
return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size;
}
3. JDK 1.8 的改动
JDK 1.7 使用分段锁机制来实现并发更新操作,核心类为 Segment,它继承自重入锁 ReentrantLock,并发度与 Segment 数量相等。
JDK 1.8 使用了 CAS 操作来支持更高的并发度,在 CAS 操作失败时使用内置锁 synchronized。
并且 JDK 1.8 的实现也在链表过长时会转换为红黑树。
LinkedHashMap
存储结构
继承自 HashMap,因此具有和 HashMap 一样的快速查找特性。
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>
内部维护了一个双向链表,用来维护插入顺序或者 LRU 顺序。
/**
* The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
accessOrder 决定了顺序,默认为 false,此时维护的是插入顺序。
final boolean accessOrder;
LinkedHashMap 最重要的是以下用于维护顺序的函数,它们会在 put、get 等方法中调用。
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { }
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }
afterNodeAccess()
当一个节点被访问时,如果 accessOrder 为 true,则会将该节点移到链表尾部。也就是说指定为 LRU 顺序之后,在每次访问一个节点时,会将这个节点移到链表尾部,保证链表尾部是最近访问的节点,那么链表首部就是最近最久未使用的节点。
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
afterNodeInsertion()
在 put 等操作之后执行,当 removeEldestEntry() 方法返回 true 时会移除最晚的节点,也就是链表首部节点 first。
evict 只有在构建 Map 的时候才为 false,在这里为 true。
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
removeEldestEntry() 默认为 false,如果需要让它为 true,需要继承 LinkedHashMap 并且覆盖这个方法的实现,这在实现 LRU 的缓存中特别有用,通过移除最近最久未使用的节点,从而保证缓存空间足够,并且缓存的数据都是热点数据。
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}
LRU 缓存
以下是使用 LinkedHashMap 实现的一个 LRU 缓存:
- 设定最大缓存空间 MAX_ENTRIES 为 3;
- 使用 LinkedHashMap 的构造函数将 accessOrder 设置为 true,开启 LRU 顺序;
- 覆盖 removeEldestEntry() 方法实现,在节点多于 MAX_ENTRIES 就会将最近最久未使用的数据移除。
class LRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
private static final int MAX_ENTRIES = 3;
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return size() > MAX_ENTRIES;
}
LRUCache() {
super(MAX_ENTRIES, 0.75f, true);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCache<Integer, String> cache = new LRUCache<>();
cache.put(1, "a");
cache.put(2, "b");
cache.put(3, "c");
cache.get(1);
cache.put(4, "d");
System.out.println(cache.keySet());
}
[3, 1, 4]
WeakHashMap
存储结构
WeakHashMap 的 Entry 继承自 WeakReference,被 WeakReference 关联的对象在下一次垃圾回收时会被回收。
WeakHashMap 主要用来实现缓存,通过使用 WeakHashMap 来引用缓存对象,由 JVM 对这部分缓存进行回收。
private static class Entry<K,V> extends WeakReference<Object> implements Map.Entry<K,V>
ConcurrentCache
Tomcat 中的 ConcurrentCache 使用了 WeakHashMap 来实现缓存功能。
ConcurrentCache 采取的是分代缓存:
- 经常使用的对象放入 eden 中,eden 使用 ConcurrentHashMap 实现,不用担心会被回收(伊甸园);
- 不常用的对象放入 longterm,longterm 使用 WeakHashMap 实现,这些老对象会被垃圾收集器回收。
- 当调用 get() 方法时,会先从 eden 区获取,如果没有找到的话再到 longterm 获取,当从 longterm 获取到就把对象放入 eden 中,从而保证经常被访问的节点不容易被回收。
- 当调用 put() 方法时,如果 eden 的大小超过了 size,那么就将 eden 中的所有对象都放入 longterm 中,利用虚拟机回收掉一部分不经常使用的对象。
public final class ConcurrentCache<K, V> {
private final int size;
private final Map<K, V> eden;
private final Map<K, V> longterm;
public ConcurrentCache(int size) {
this.size = size;
this.eden = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(size);
this.longterm = new WeakHashMap<>(size);
}
public V get(K k) {
V v = this.eden.get(k);
if (v == null) {
v = this.longterm.get(k);
if (v != null)
this.eden.put(k, v);
}
return v;
}
public void put(K k, V v) {
if (this.eden.size() >= size) {
this.longterm.putAll(this.eden);
this.eden.clear();
}
this.eden.put(k, v);
}
}
参考资料
- Eckel B. Java 编程思想 [M]. 机械工业出版社, 2002.
- Java Collection Framework
- Iterator 模式
- Java 8 系列之重新认识 HashMap
- What is difference between HashMap and Hashtable in Java?
- Java 集合之 HashMap
- The principle of ConcurrentHashMap analysis
- 探索 ConcurrentHashMap 高并发性的实现机制
- HashMap 相关面试题及其解答
- Java 集合细节(二):asList 的缺陷
- Java Collection Framework – The LinkedList Class
